Kidney Dialysis in Bathinda: Comprehensive Guide to Treatment and Care
Kidney dialysis is a life-saving treatment for individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) who have lost most or all of their kidney function. In Bathinda, advanced medical facilities and expert nephrologists provide high-quality dialysis care. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about kidney dialysis in Bathinda, from understanding the procedure to the types of dialysis available, and the benefits of seeking treatment in this city.

What Is Kidney Dialysis?
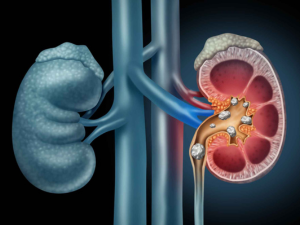
Kidney dialysis is a medical procedure that replicates the essential functions of healthy kidneys, filtering waste, excess fluid, and toxins from the blood. This treatment is necessary for patients whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions effectively due to severe kidney damage or failure.
Types of Kidney Dialysis
1. Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is the most common type of dialysis. It involves using a machine to filter the blood. Here’s how it works:
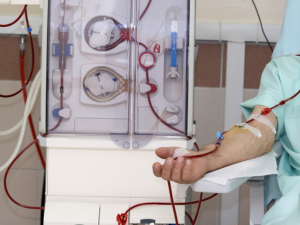
- Vascular Access : A surgeon creates a vascular access, usually in the arm, which allows blood to travel from the body to the dialysis machine.
- Dialysis Machine: Blood is pumped from the body into the machine, where it passes through a series of filters known as a dialyzer or artificial kidney.
- Filtering Process: The dialyzer removes waste products and excess fluids from the blood.
- Return of Clean Blood: The filtered blood is then returned to the body.
Patients typically undergo hemodialysis three times a week, with each session lasting about four hours.
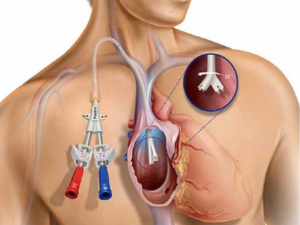
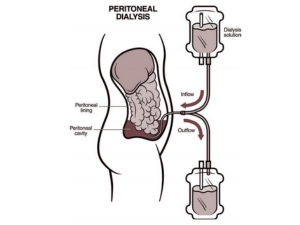
2. Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of the abdomen, known as the peritoneal membrane, to filter blood. The process involves:
- Catheter Placement: A catheter is surgically placed into the abdomen.
- Dialysis Solution: A sterile dialysis solution is introduced into the abdominal cavity through the catheter.
- Waste Removal: The solution absorbs waste products and excess fluids from the blood vessels in the peritoneal membrane.
- Draining: The solution is then drained from the abdomen and replaced with fresh solution.
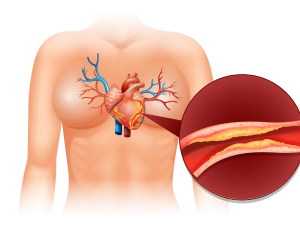
Causes and Risk Factors for Kidney Failure
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys over time, leading to kidney failure.
- Hypertension: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can cause damage to the kidneys’ blood vessels, impairing their function.

- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Progressive loss of kidney function over time can eventually lead to kidney failure.
Benefits of Kidney Dialysis
Dialysis offers numerous benefits, especially for those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD):
- Extended Life Expectancy: Dialysis significantly prolongs the lives of individuals with kidney failure.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients can maintain a relatively normal lifestyle and continue daily activities.
- Flexibility: Peritoneal dialysis offers the flexibility of home treatment, which can be more convenient for patients.
- Preparation for Transplant: Dialysis keeps patients healthy while they await a kidney transplant.
The Dialysis Procedure
The dialysis procedure, whether hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, requires careful preparation and ongoing management.
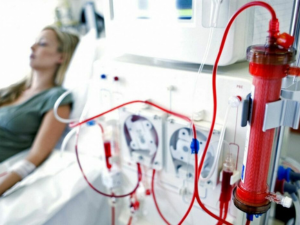
- Preparation: Before starting hemodialysis, a vascular access is created. This access point, usually in the arm, is crucial for the efficient flow of blood to and from the dialysis machine.
- Dialysis Session: During each session, the patient is connected to the dialysis machine. Blood is drawn from the body, filtered through the dialyzer, and returned to the body.
- Post-Session Care: After each session, the patient’s vital signs are monitored. It’s essential to maintain good hygiene and care for the vascular access site to prevent infections.
Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure
- Preparation: Before starting hemodialysis, a vascular access is created. This access point, usually in the arm, is crucial for the efficient flow of blood to and from the dialysis machine.
- Dialysis Session: During each session, the patient is connected to the dialysis machine. Blood is drawn from the body, filtered through the dialyzer, and returned to the body.
- Post-Session Care: After each session, the patient’s vital signs are monitored. It’s essential to maintain good hygiene and care for the vascular access site to prevent infections.
Living with Dialysis
Diet and Nutrition
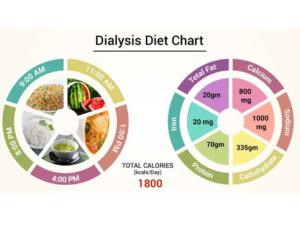
- Balanced Diet: Follow a kidney-friendly diet low in sodium, potassium, and phosphorus.
- Fluid Management: Monitor and limit fluid intake to prevent excess fluid buildup.
- Protein Intake: Ensure adequate protein intake to maintain muscle mass and overall health.
Regular Monitoring
- Health Check-ups: Regular check-ups with your nephrologist are crucial to monitor kidney function and overall health.
- Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications as directed to manage blood pressure, anemia, and other conditions associated with kidney disease.
Emotional Support
- Counseling: Seek counseling or join support groups to cope with the emotional challenges of living with dialysis.
- Family Support: Involve family members in your care plan for additional support and encouragement.
Conclusion
Kidney dialysis in Bathinda has evolved to provide patients with advanced, comprehensive care. With state-of-the-art facilities and a dedicated healthcare team, patients can manage kidney disease effectively and maintain a good quality of life. By understanding the types of dialysis, the procedure, and the available local facilities, patients and their families can make informed decisions about their care.
Living with dialysis requires commitment and lifestyle adjustments, but with the right support and resources, individuals with kidney disease can lead fulfilling lives. Bathinda’s dialysis centers are at the forefront of providing this essential care, ensuring that patients receive the best possible treatment and support.